How To Update Branch From Another Branch
Apply changes from one Git branch to another
In Git, there are several ways to integrate changes from one branch into another:
-
Merge branches
-
Rebase branches
-
Utilise divide commits from i co-operative to another (carmine-pick)
-
Utilize separate changes from a commit
-
Apply specific file to a co-operative
Merge branches
Suppose you have created a characteristic branch to work on a specific task, and want to integrate the results of your piece of work into the principal code base later you lot have completed and tested your feature:

Merging your co-operative into master is the almost common way to do this.
It is very common that while you are working in your feature branch, your teammates go along to commit their piece of work to master:

When y'all run merge, the changes from your feature branch are integrated into the HEAD of the target branch:

Git creates a new commit (Chiliad) that is referred to as a merge commit that results from combining the changes from your feature branch and master from the point where the 2 branches diverged.
Merge branches
-
In the Branches popup (main carte ) or in the Branches pane of the Git tool window , select the target branch that y'all want to integrate the changes to, and choose Checkout from the context menu to switch to that co-operative.
-
Do i of the following:
-
If you do not need to specify options for the merge, select the branch that you lot desire to merge into the current branch and cull Merge into Current from the submenu.
-
If you demand to specify merge options, from the principal menu cull to open up the Merge dialog:
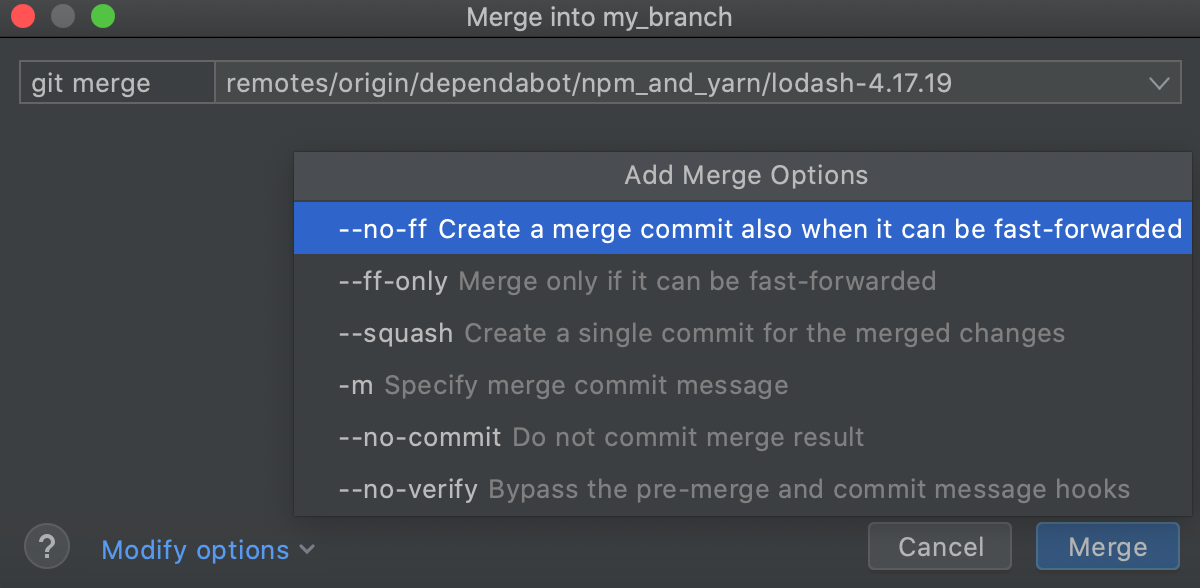
Select the co-operative that you want to merge into the current branch, click Modify options and choose from the following:
-
--no-ff: a merge commit will be created in all cases, fifty-fifty if the merge could be resolved as a fast-forward. -
--ff-but: the merge volition be resolved merely if information technology is possible to fast-forward. -
--squash: a single commit with all pulled changes will exist created on meridian of the current co-operative. -
-grand: yous will exist able to edit the message for the merge commit. -
--no-commit: a merge volition exist performed, but a merge commit will not be created so that y'all can inspect the result of the merge earlier committing.
-
Click Merge.
-
If your working tree is make clean (which ways you have no uncommitted changes), and no conflicts occur between your feature branch and the target branch, Git will merge the 2 branches, and the merge commit will appear in the Log tab of the Git tool window Alt+9:
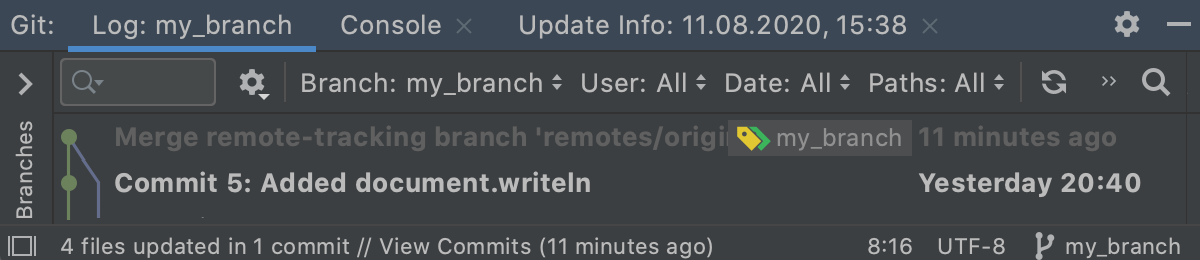
If conflicts occur between your branch and the target co-operative, you volition be prompted to resolve them (see Resolve conflicts). If there are unresolved conflicts left later on a merge, the Merge Conflicts node volition announced in the corresponding changelist in the Local Changes view with a link to resolve them.
If you have local changes that will be overwritten by merge, WebStorm will suggest performing Smart merge. If you lot select this choice, WebStorm will stash uncommitted changes, perform merge, and then unstash the changes.
Rebase branches (git-rebase)
When you rebase a branch onto some other branch, yous utilize the commits from the beginning branch on pinnacle of the Caput commit in the 2d branch.
Suppose you have created a feature branch to piece of work on a specific task and make several commits to that branch:

While yous develop in your branch, your teammates proceed to commit their work to master:

When you perform the rebase operation you integrate changes you accept done in your feature branch to the master co-operative by applying your commits on pinnacle of the electric current Head commit in master:

Rebase a co-operative on top of another branch
-
From the main carte du jour select :
-
From the listing, select the target co-operative onto which you lot want to rebase the current branch:
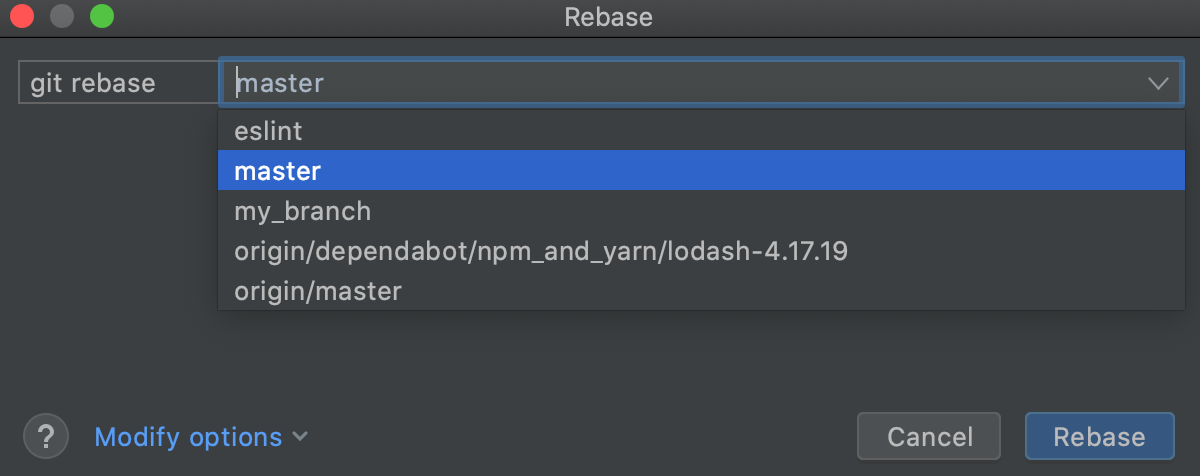
-
If you need to rebase the source branch starting from a item commit instead of rebasing the entire branch, click Change options and cull --onto. In the source branch field, enter the hash of the commit starting from which you want to apply the current branch to the new base:
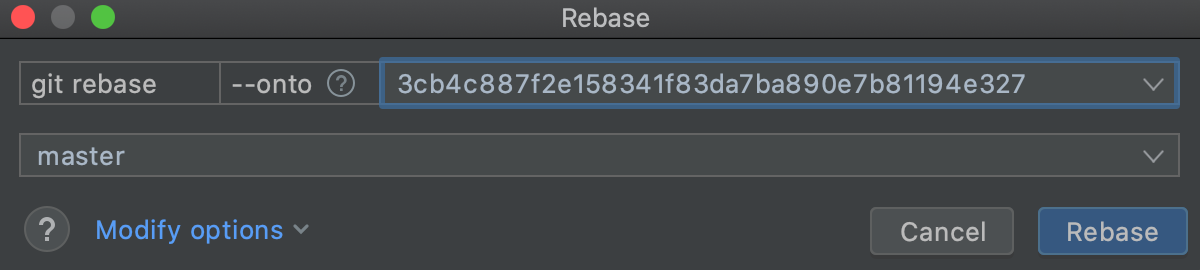
-
If the branch you want to rebase is not currently checked out, click Change options, click Select another co-operative to rebase, and choose a branch from the list that appears:
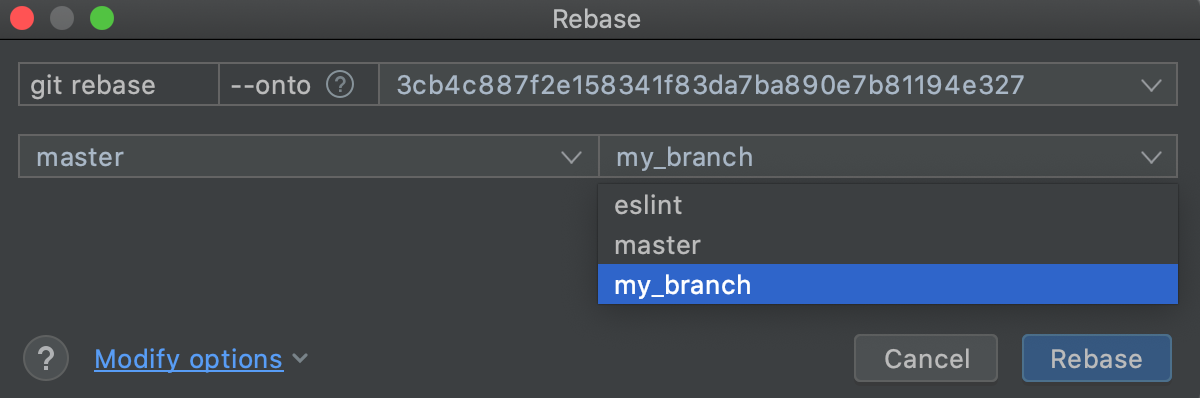
WebStorm will cheque out this branch before starting the rebase functioning.
-
If yous desire to rebase all commits reachable in the branch, click Alter options and choose --root (for more information on this option, encounter git-rebase).
-
If you demand to keep empty commits, which are commits that practice not change anything from their parent, click Modify options and choose --keep-empty (for more data on this choice, encounter git-rebase).
-
If you desire to preserve merge commits during the rebase for the sake of keeping them in the branch history, click Modify options and cull --preserve-merges (this pick is unavailable for
interactiverebase). -
Click Rebase.
If you do not need to specify options for the rebase, you tin initiate a rebase without invoking the rebase dialog. In the Branches popup or in the Branches pane of the Git tool window select a branch and cull 1 of the following actions:
-
Pull into Electric current Using Rebase (for remote branches) to fetch changes from the selected branch and rebase the current branch on top of these changes.
-
Checkout and Rebase onto Electric current (for both remote and local branches) to cheque out the selected co-operative and rebase information technology on elevation of the branch that is currently checked out. If the remote co-operative doesn't exist locally, WebStorm will silently create a tracked local co-operative, checkout into information technology and rebase.
-
Rebase Current onto Selected (for both remote and local branches) to rebase the branch that is currently checked out on top of the selected.
For details on how to skip or squash commit during a rebase, refer to Edit projection history by performing interactive rebase.
Picket this video to see how a merge or a rebase functioning are reflected in the Log tab of the Git tool window Alt+9:
Cherry-pick divide commits
Sometimes you simply need to apply a unmarried commit to a unlike branch instead of rebasing or merging an entire branch. This may be useful, for example, if yous are working in a feature branch and want to integrate a hotfix from master that was committed later on the ii branches have diverged. Or you may want to backport a fix to a previous release branch. You lot can do so by using the Cherry-pick action.
The condition of a ruby-red pick performance is displayed in the status bar. Y'all can ever abort an ongoing cherry-choice past selecting Abort Crimson-Pick in the Git Branches popup.
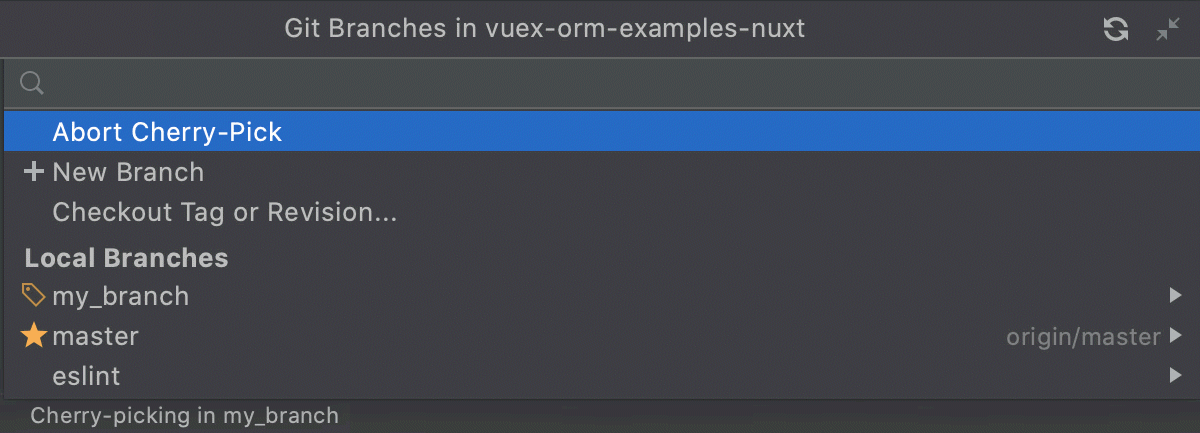
Apply a commit to another branch
-
In the Branches popup (primary menu ), select the target co-operative that you want to integrate the changes to and choose Checkout from the popup menu to switch to that branch.
-
Open the Git tool window Alt+nine and switch to the Log tab.
-
Locate the commit containing the changes yous want to cherry pick.
You can filter commits by branch, user or date. Yous tin also click
on the toolbar and select Highlight | Non-Picked Commits option to gray out the commits that have already been applied to the current branch. If you know the commit hash, or are looking for a tagged commit, yous can also use the Go to Hash / Co-operative / Tag activeness (press Ctrl+F in the Log tab of the Git tool window Alt+nine, or click
on the toolbar).
-
Select the required commit. Utilise the information in the Commit Details expanse to make sure these are the changes you want to transfer to another branch.
-
Click Cherry-selection
on the toolbar. WebStorm will apply and commit changes to the target co-operative.
-
If the cherry-selection failed with conflicts, the selected changes will appear in Changes expanse that you lot tin can see in the Local Changes view. You can review these changes and commit them later if necessary.
If you want WebStorm to create changelists automatically in case of scarlet-pick fail, switch on the corresponding setting in .
-
Push the changes to the target co-operative.
Apply separate changes
Imagine you've made some changes to a file that y'all want to apply to a different branch, simply these changes were committed together with other modified files. WebStorm lets yous apply divide changes instead of cherry-picking an unabridged commit.
-
In the Branches popup (main menu ), select the target branch that you want to integrate the changes to and choose Checkout from the popup carte to switch to that branch.
-
Open the Git tool window Alt+9 and switch to the Log tab.
-
Locate the commit that contains the changes that yous want to employ.
You lot can filter commits by branch, user or date. Y'all can also click
on the toolbar and select Highlight | Non-Picked Commits option to grey out the commits that accept already been applied to the current branch. If yous know the commit hash, or are looking for a tagged commit, you can also use the Go to Hash / Branch / Tag action (press Ctrl+F in the Log tab of the Git tool window Alt+9, or click
on the toolbar).
-
In the Commit details pane on the right, select the files containing the changes you want to apply to the target branch and select Red-Pick Selected Changes from the context menu.
-
In the dialog that opens, select an existing changelist or enter the name for a new changelist and click OK.
-
Commit the changes and so push them to the target branch.
Apply split up files
In improver to applying separate changes to a unmarried file, you can copy an entire file's contents to a different branch. This may be useful, for case, if the file you lot want to utilise doesn't exist in the target branch, or if changes to information technology were made inside several commits.
-
Switch to the branch to which the changes volition exist applied.
-
In the Branches popup (main carte ) or in the Branches pane of the Git tool window , select the branch that contains the file you want to apply and choose Prove Diff with Working Tree from the context menu.
The Changes tool window that opens shows a list of all files that are different in the selected co-operative compared with the branch that is currently checked out:
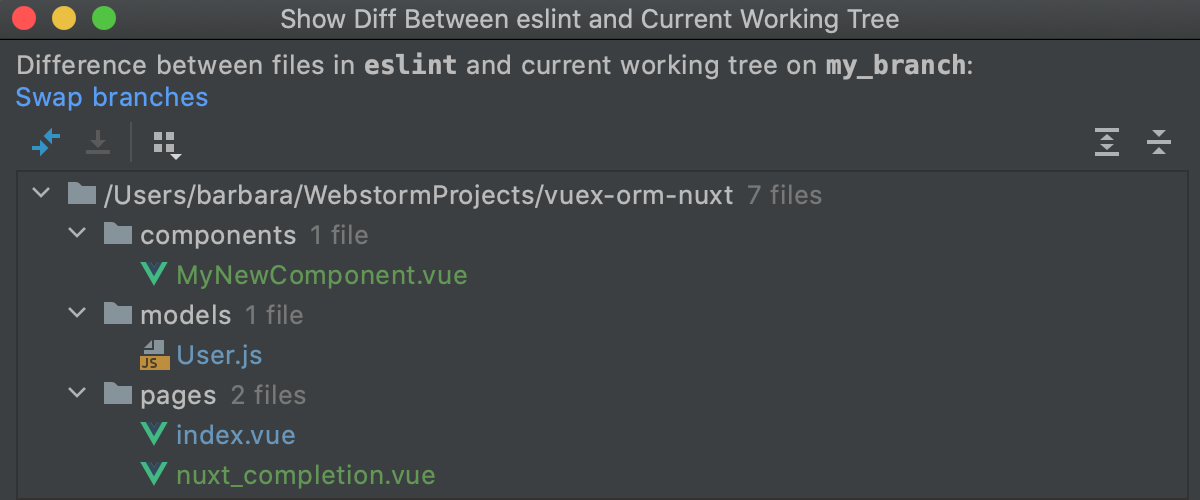
-
Files that exist in the selected branch and are missing in the current branch are marked with grey.
-
Files that exist in the electric current branch but are missing in the selected co-operative are marked with green.
-
Files that contain differences between the selected and the electric current branch are marked with blue.
Yous can click the Swap Branches link to change which branch is considered as a base confronting which you are comparing the other branch.
-
-
Select the file that you want to apply to the current co-operative, and choose Get from Branch from the context menu or click
on the toolbar .
-
Commit and button the changes. WebStorm will copy the entire contents of the file to the current branch.
Last modified: 28 May 2022
Source: https://www.jetbrains.com/help/webstorm/apply-changes-from-one-branch-to-another.html
Posted by: wilsonsqueseseen1989.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Update Branch From Another Branch"
Post a Comment